
Physics 101, Physics Formulas, Science Fair Projects, Science Lessons, Physics Projects, School
A sound wave with the beat pattern in diagram D will have a volume that varies at a regular rate - you can hear a pulse or flutter in the sound. Sound waves and pitch. Because sound travels outwards from a central source, waves interact in interesting patterns. When the same pitch or frequency sound wave is produced from two sources, a.
How To Calculate Frequency Of A Waveform Haiper
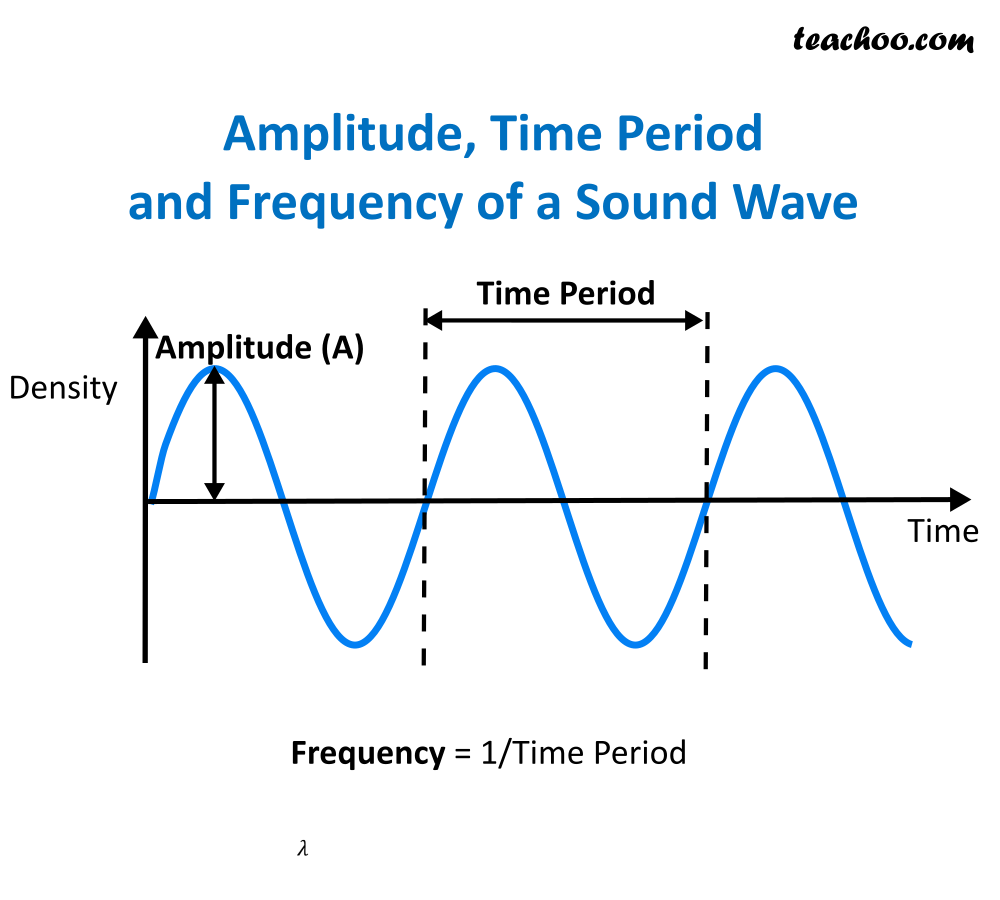
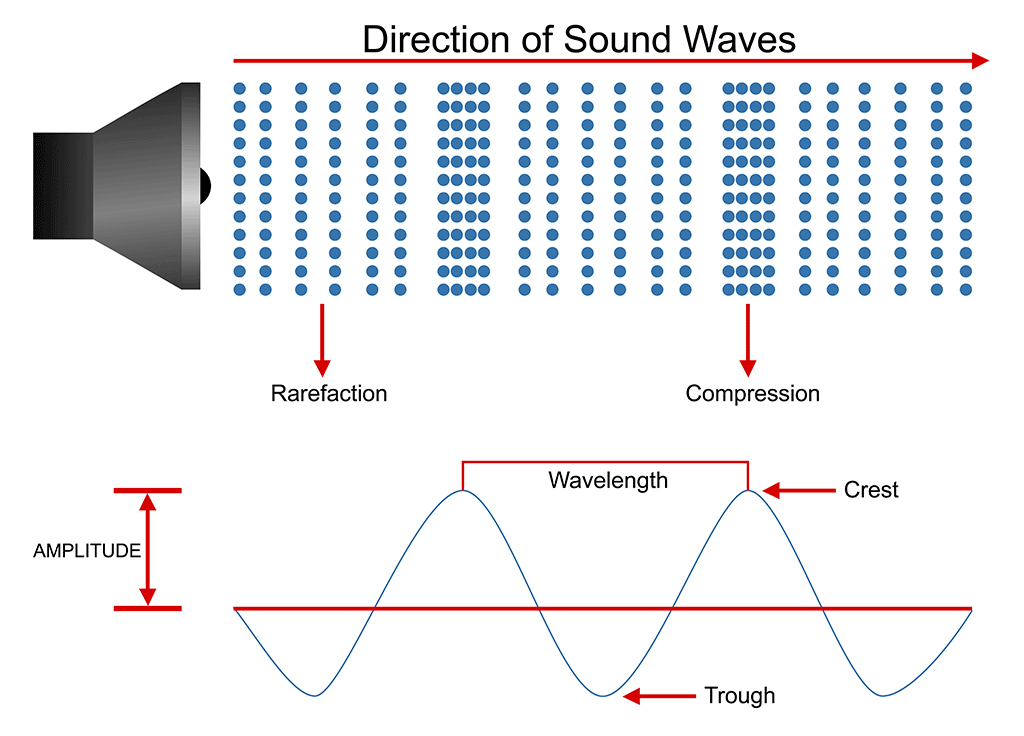
One such property is amplitude. The amplitude of a wave refers to the maximum amount of displacement of a particle on the medium from its rest position. In a sense, the amplitude is the distance from rest to crest. Similarly, the amplitude can be measured from the rest position to the trough position.

Amplitude, Frequency and Time Period of Sound Teachoo Concepts
The diagram below shows a sound wave reflecting off the sea bed; knowing the time taken for the reflection to occur and the speed of sound in water, allows the captain to calculate the depth of the water. This technique is known as echo sounding. Transmission of sound.

What is Sound Wave Mike Migas Production
Amplitude Amplitude in light refers to the amount of energy in an electromagnetic wave and its meaning is the same here. Amplitude refers to the distance of the maximum vertical displacement of the wave from its mean position. Larger the amplitude, the higher the energy.

15.3 Hearing Anatomy & Physiology
Waves > Sound Introduction to sound review Google Classroom Review the key terms and skills for sound waves, including how to identify the nodes and antinodes for standing waves in tubes. Key terms Standing sound waves open and closed tubes Sound waves are longitudinal waves in a medium such as air.

Class 9 Sound Notes BrainIgniter
Interactive This video shows waves on the surface of a wine glass, being driven by sound waves from a speaker. As the frequency of the sound wave approaches the resonant frequency of the wine glass, the amplitude and frequency of the waves on the wine glass increase. When the resonant frequency is reached, the glass shatters.

Draw a diagram depicting soft sound and a louder soundb.what is the main difference between the
Key points. A sound wave is a vibration that travels through a solid, liquid or gas such as the air or water. A loud sound has a large amplitude, a high pitched sound has a high frequency.

Loudness, Intensity, Pitch and Quality of Sound Teachoo
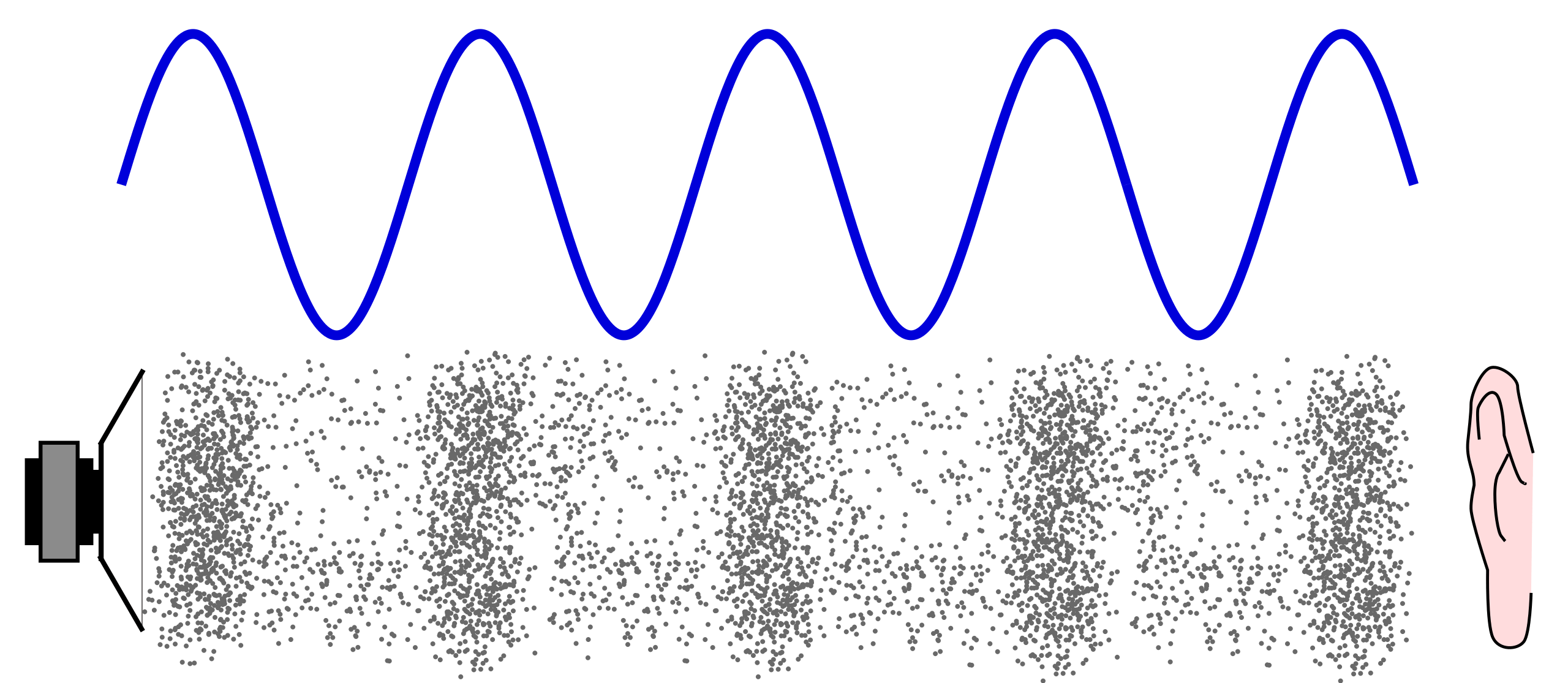
Sound is a pressure wave caused when something vibrates, making particles bump into each other and then apart. The particles vibrate back and forth in the. READ MORE MORE TEACHER PLD Building Science Concepts: Exploring sound Use music to engage students in learning the science concepts of sound in a fun and meaningful way.
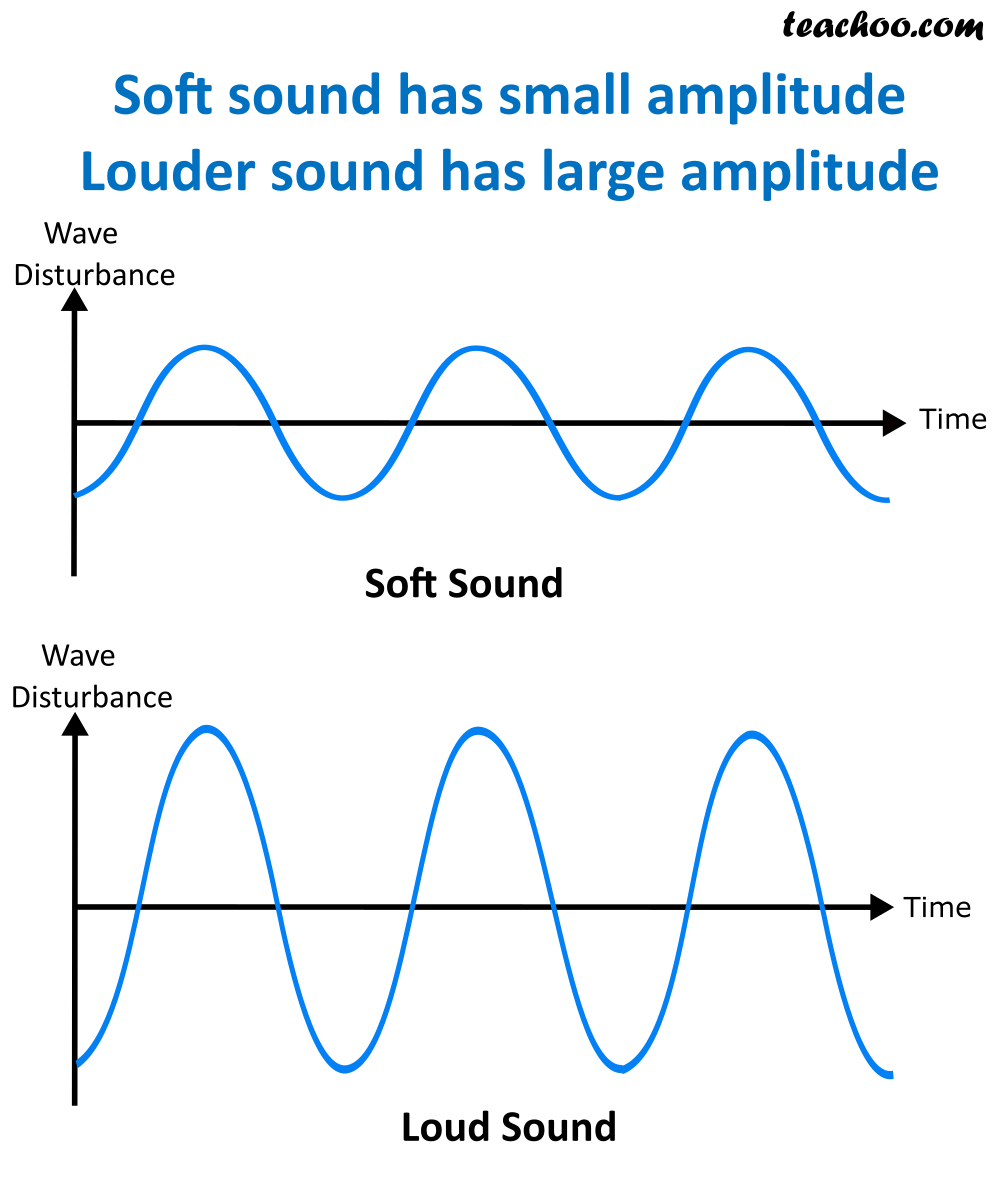
Loudness, Intensity, Pitch and Quality of Sound Teachoo
The five main characteristics of sound waves include wavelength, amplitude, frequency, time period and velocity. Learn all these characteristics in detail here.. Taking reference from the above diagram, the distance between two consecutive compressions or rarefaction is called the wavelength of the sound. It is also sometimes referred to as.
Sound Science Great Headphones Blend Physics, Anatomy and Psychology
Google Classroom We've all heard that there's no sound in space, even though tons of movies and TV shows have you hearing everything from ships' engines to explosions. If there's sound on Earth, why wouldn't there be sound in space? The secret is in how sound travels. How does sound travel?
Sound Waves PASCO
A vibrating object A material for the sound wave to travel through, such as air (we call this a medium) Something to detect the sound e.g. your ear Sound can pass through: Solids e.g..

Amplitude, Frequency and Time Period of Sound Teachoo Concepts
A speaker produces a sound wave by oscillating a cone, causing vibrations of air molecules. In Figure 17.2. 2, a speaker vibrates at a constant frequency and amplitude, producing vibrations in the surrounding air molecules. As the speaker oscillates back and forth, it transfers energy to the air, mostly as thermal energy.

5 Ways to Make Propagation of Sound an Approachable Topic
Infrasonic Waves (Infrasound) Infrasonic waves have frequencies below 20 Hz, which makes them inaudible to the human ear. Scientists use infrasound to detect earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, to map rock and petroleum formations underground, and to study activity in the human heart.

Wavelength of Sound Waves Class 9 Science Notes by Teachoo
Sound Wave Generator Generate a personalized sound wave art in seconds Upload your audio, search for your favorite song, or pick one from Spotify and let our sound wave maker help you create stunning sound waves. Start Designing No sign-up is required. Want some inspiration to get started? Space

Wavelength of Sound Waves Class 9 Science Notes by Teachoo
UCD: Physics 9B - Waves, Sound, Optics, Thermodynamics, and Fluids 1: Waves 1.2: Wave Properties Expand/collapse global location 1.2: Wave Properties. and is called the wavelength of the wave. A glance at the two diagrams above should make it clear that the wavelength is a universal feature of that particular wave, and does not depend upon.
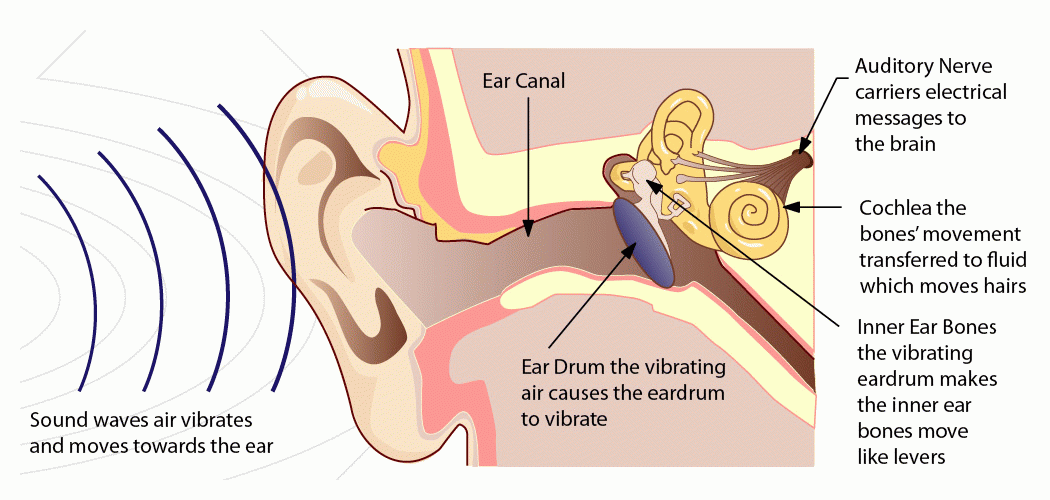
What is Sound? Understanding the Nature of Sound and Soundwaves.
Resource Add to collection Sound is a form of energy that is caused by the vibration of matter. Sound is transmitted through waves, which travel through solids, liquids and gases. We are most used to the sound travelling through air, but sound is able to travel faster and further in solids and liquids. 'Seeing' sound